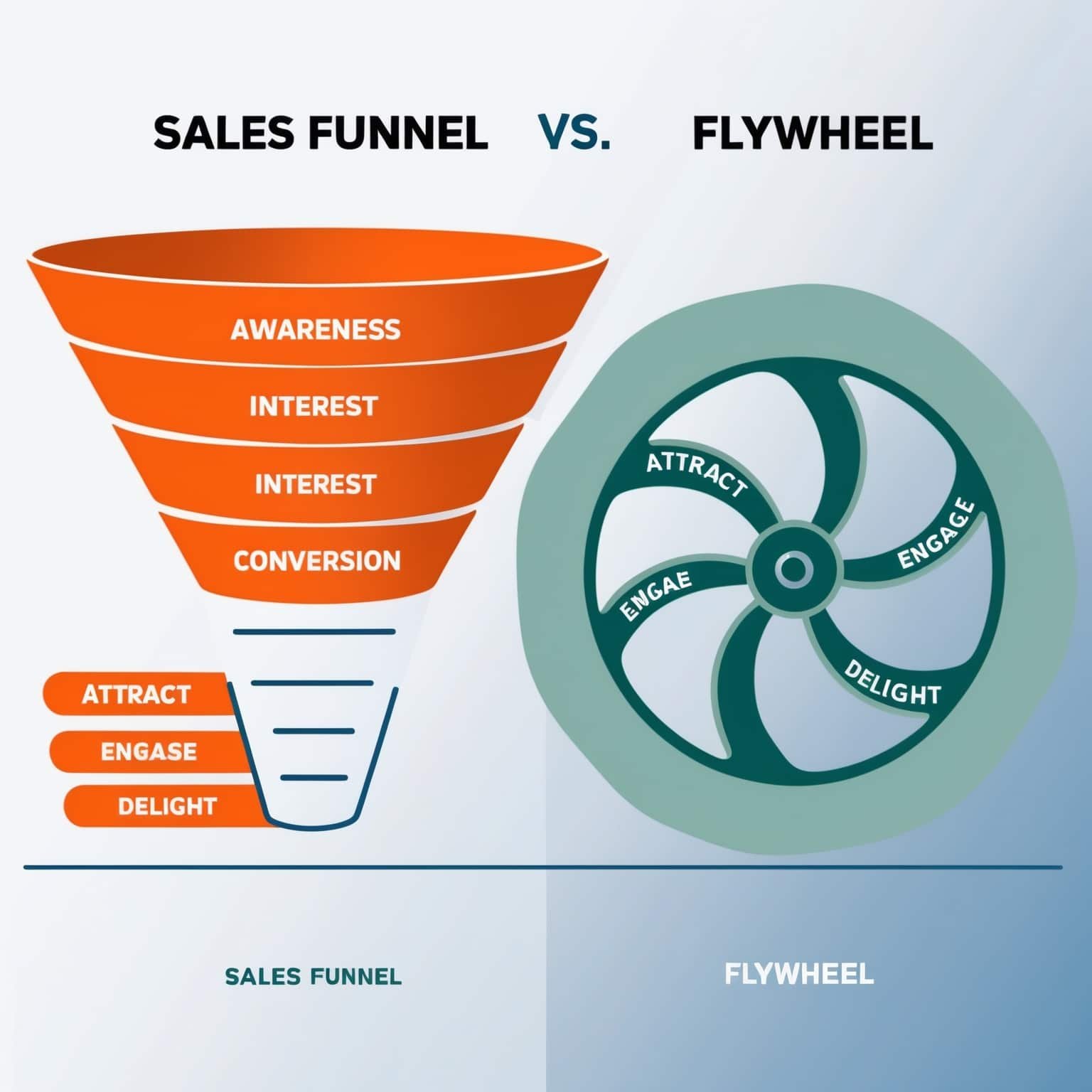
Sales Funnel Vs Flywheel? Sales Funnel and Flywheel are two popular models in marketing. Both aim to attract and retain customers, but they work differently.
Understanding these models helps businesses improve their strategies. The Sales Funnel focuses on guiding prospects through stages until they become customers. It has a clear start and end point. On the other hand, the Flywheel emphasizes continuous customer engagement. It relies on customer satisfaction to drive growth.
This model keeps spinning, fueled by happy customers who bring in new ones. Comparing these approaches can clarify which might suit your business better. It helps in choosing the right strategy to boost customer acquisition and retention. So, let’s dive deeper into the Sales Funnel and Flywheel to see their unique strengths and differences.
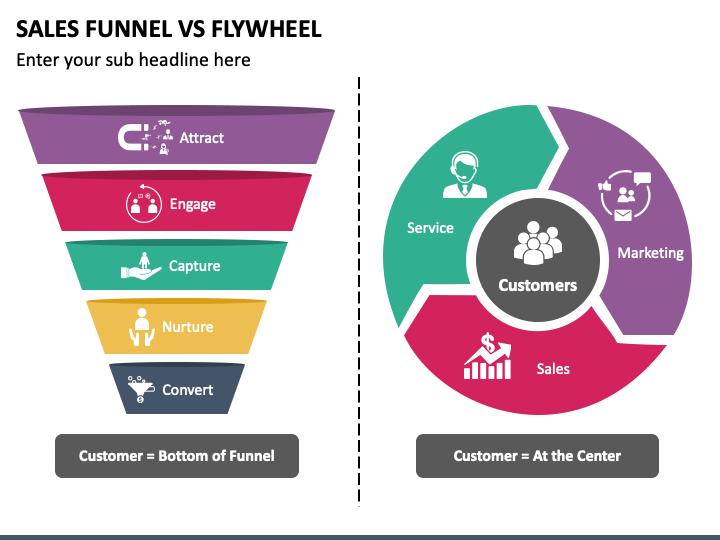
Credit: www.sketchbubble.com
Introduction To Sales Funnel And Flywheel
The Sales Funnel and Flywheel are two models used in marketing and sales. They help businesses understand and improve their customer journey. Each model has its unique approach and benefits. Understanding both can help you choose the right strategy for your business.
Concept Of Sales Funnel
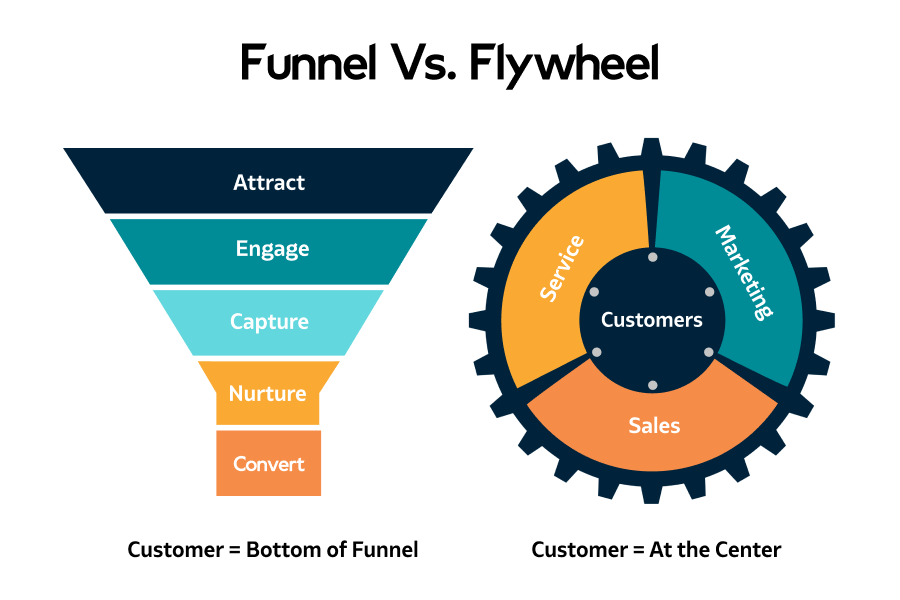
The Sales Funnel is a traditional model. It visualizes the steps a customer takes from awareness to purchase. The funnel is wide at the top and narrows down. This represents the gradual decrease in potential customers through each stage.
Here are the main stages of a typical Sales Funnel:
- Awareness: Potential customers become aware of your product.
- Interest: They show interest and seek more information.
- Consideration: They evaluate and compare your product with others.
- Intent: They show intent to purchase.
- Purchase: They make the actual purchase.
Concept Of Flywheel
The Flywheel model focuses on customer experience and retention. It visualizes the continuous cycle of attracting, engaging, and delighting customers. Unlike the funnel, the flywheel does not have an end. It emphasizes keeping customers happy so they become promoters of your brand.
The Flywheel has three main phases:
- Attract: Draw in new customers with valuable content.
- Engage: Build relationships and keep them interested.
- Delight: Ensure customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The Flywheel relies on the momentum created by happy customers. They drive referrals and repeat business. This creates a self-sustaining cycle of growth.
Historical Context
The sales funnel and flywheel models have different origins. Understanding their history helps us see their benefits. Let’s explore how each came to be.
Evolution Of Sales Funnel
The sales funnel concept started in the late 1800s. It was first introduced by E. St. Elmo Lewis. He created the AIDA model: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. This model explained how customers moved through stages before buying.
Over time, the sales funnel became a standard. Businesses used it to guide their sales processes. The funnel helped identify potential customers and convert them into buyers. It focused on moving leads through a linear path.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Attention | Attracting potential customers |
| Interest | Engaging them with information |
| Desire | Creating a want for the product |
| Action | Encouraging the purchase |
Rise Of The Flywheel Model
The flywheel model is newer. HubSpot introduced it in 2018. The flywheel emphasizes customer satisfaction. It shows how happy customers drive growth.
Unlike the funnel, the flywheel is circular. It focuses on three main stages: Attract, Engage, and Delight. This model puts customers at the center. The energy from happy customers keeps the wheel spinning.
- Attract: Draw in potential customers.
- Engage: Build relationships and trust.
- Delight: Provide exceptional service.
The flywheel reflects modern business needs. It values long-term customer relationships over one-time sales. This approach leads to sustainable growth and loyal customers.
Key Components Of Sales Funnel
The sales funnel is a powerful tool for guiding potential customers. It consists of several stages, each essential for converting leads into loyal customers. Understanding these stages helps businesses develop effective marketing strategies. Let’s explore the key components of the sales funnel.
Awareness Stage
The Awareness Stage is the first step in the sales funnel. Here, potential customers become aware of your product or service. This stage focuses on attracting attention and generating interest. Effective strategies include:
- Blog posts
- Social media campaigns
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
Creating valuable content is crucial. It helps build trust and credibility. Use engaging headlines and clear, concise information to capture interest.
Consideration Stage
In the Consideration Stage, leads have shown interest. They are now evaluating their options. Your goal is to provide detailed information. This helps them make an informed decision. Effective strategies include:
- Email marketing
- Webinars and demos
- Case studies and testimonials
Focus on addressing pain points. Highlight the benefits and unique features of your product. Provide comparisons and evidence of success.
Decision Stage
The Decision Stage is critical. At this point, leads are ready to make a purchase. Your objective is to facilitate a smooth transaction. Effective strategies include:
- Free trials or samples
- Special offers and discounts
- Personalized follow-ups
Ensure the purchasing process is easy and clear. Provide excellent customer support. Encourage positive reviews and referrals.
Understanding the components of the sales funnel helps optimize your marketing efforts. Each stage requires specific strategies to nurture leads effectively.
Key Components Of Flywheel
The flywheel model is a modern approach to customer acquisition and retention. This model focuses on creating momentum and continuously engaging customers. Unlike the traditional sales funnel, the flywheel emphasizes a cyclical process. It has three key components: Attract, Engage, and Delight.
Attract Phase
The Attract Phase is about drawing potential customers to your brand. Use valuable content and resources to capture their attention. This can include:
- Blog posts
- Social media content
- SEO-optimized articles
- Informative videos
Focus on addressing your audience’s needs and pain points. Provide solutions and insights. This builds trust and interest in your brand.
Engage Phase
The Engage Phase aims to create meaningful interactions with your audience. It’s about building relationships and nurturing leads. Key strategies in this phase include:
- Email marketing
- Personalized communication
- Interactive content
- Webinars and workshops
Ensure that your communication is relevant and valuable. Engage your audience through multiple touchpoints. This keeps them interested and moves them closer to making a purchase.
Delight Phase
The Delight Phase focuses on ensuring customer satisfaction. Happy customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates. Ways to delight your customers include:
- Exceptional customer service
- Personalized follow-ups
- Exclusive offers and rewards
- Collecting and acting on feedback
Delighted customers spread positive word-of-mouth. This fuels the flywheel, attracting more customers and creating a cycle of growth.
Comparison Of Models
The Sales Funnel and Flywheel models are two ways to understand customer journeys. Both have unique approaches to customer acquisition and customer retention. Let’s compare these models.
Customer Acquisition
The Sales Funnel focuses on moving potential customers through stages:
- Awareness
- Interest
- Decision
- Action
It narrows down from many prospects to a few buyers. The funnel starts wide and gets narrower.
The Flywheel model treats acquisition differently. It relies on customer delight to attract new customers.
Happy customers spread the word, bringing in new prospects. This model focuses on continuous momentum.
Customer Retention
In the Sales Funnel, the focus is mainly on getting new customers. Once a sale happens, the process ends.
Retention is sometimes an afterthought. This model can miss opportunities for repeat business.
The Flywheel model places customer retention at its core. It views customers as ongoing relationships.
Happy customers help drive the flywheel, creating a cycle of retention and acquisition.
| Aspect | Sales Funnel | Flywheel |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | New Customers | Customer Delight |
| Process | Linear | Circular |
| Customer Role | End of Journey | Part of Journey |
Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right model. The goal is to create happy, loyal customers.
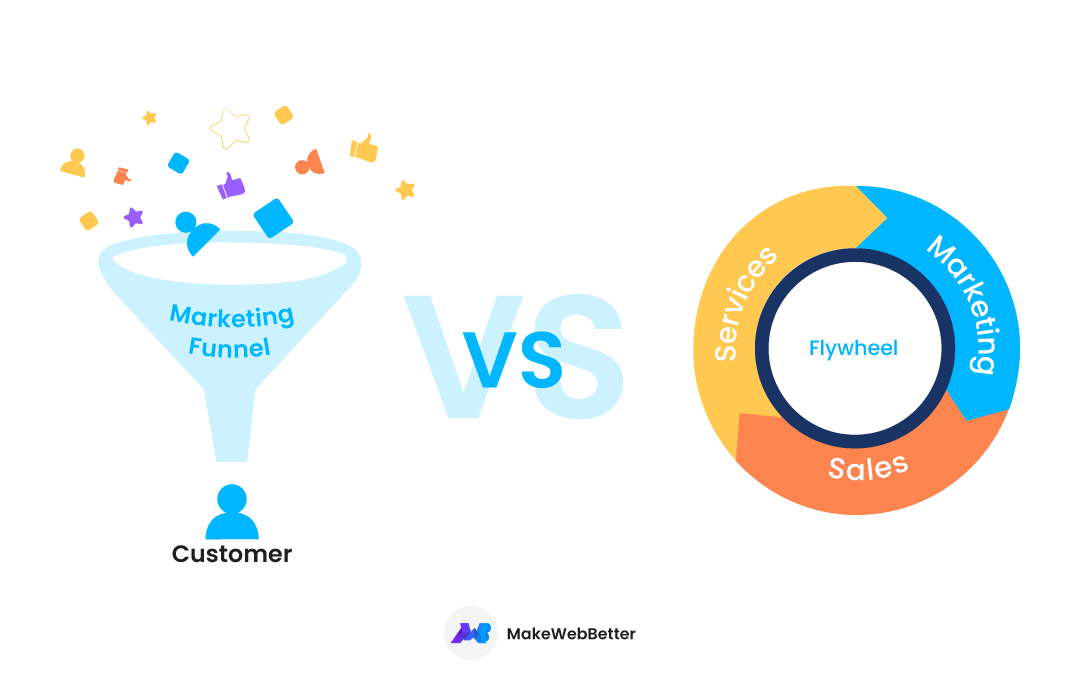
Credit: makewebbetter.com
Pros And Cons Of Sales Funnel
Understanding the pros and cons of a sales funnel can help businesses decide if this model suits their needs. The sales funnel has been a traditional approach in marketing, guiding potential customers from awareness to purchase. It is essential to consider both the strengths and weaknesses of this model for better decision-making.
Advantages
The sales funnel offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for many businesses.
- Structured Process: The sales funnel provides a clear path for potential customers. This helps businesses understand where prospects are in their buying journey.
- Targeted Marketing: Each stage of the funnel allows for specific marketing strategies. This ensures that messages are tailored to the audience’s needs.
- Performance Tracking: Businesses can track conversion rates at each stage. This helps identify which areas need improvement.
- Forecasting Sales: The funnel helps predict future sales based on the number of leads at each stage. This aids in better planning and resource allocation.
- Focused Efforts: Marketers can focus efforts on high-potential leads. This increases efficiency and effectiveness in closing deals.
Disadvantages
While the sales funnel has its strengths, it also has some drawbacks.
- Linear Approach: The funnel assumes a linear journey, which is not always the case. Customers may take a non-linear path, making this model less accurate.
- Customer Drop-off: Many potential customers drop off at each stage. This can result in a low conversion rate from leads to actual sales.
- Limited Engagement: The funnel focuses on guiding customers to purchase. It does not emphasize post-purchase engagement, which is crucial for customer retention.
- Time-Consuming: Managing and optimizing each stage of the funnel can be time-consuming. This may require significant resources and effort.
- Over-Simplification: The funnel may oversimplify the buying process. This can lead to missed opportunities for deeper customer interactions.
Pros And Cons Of Flywheel
The Flywheel model has gained traction in marketing circles. It emphasizes customer retention and satisfaction. This model, unlike the traditional sales funnel, is continuous and cyclical. Understanding its pros and cons can help businesses decide if it’s the right approach.
Advantages
The Flywheel model boasts several advantages for businesses. It focuses on customer experience, ensuring long-term loyalty and retention.
- Customer-Centric: The Flywheel model revolves around the customer. It enhances customer satisfaction through continuous engagement.
- Sustainable Growth: This model encourages sustainable growth by leveraging customer referrals and repeat purchases.
- Efficiency: By focusing on existing customers, businesses can reduce acquisition costs.
- Momentum: As more customers get satisfied, the momentum increases. It attracts new customers through positive word-of-mouth.
Disadvantages
Despite its benefits, the Flywheel model has some disadvantages. It might not be suitable for all business types.
- Initial Setup: Implementing the Flywheel model requires significant initial setup. It includes aligning all departments and systems.
- Time-Consuming: Building momentum and achieving results can take time. It requires consistent effort and patience.
- Complexity: The model’s continuous nature can be complex to manage. It requires seamless coordination among different teams.
- Resource Intensive: Focusing on customer retention demands substantial resources. It includes dedicated teams and advanced tools.
Choosing The Right Model
Deciding between the sales funnel and the flywheel model can be daunting. Each has its strengths and suits different business needs. Understanding your business type and growth stage can help you choose the right model.
Business Type Considerations
Different businesses have different needs. Here’s a quick guide:
| Business Type | Best Model |
|---|---|
| B2B (Business to Business) | Sales Funnel |
| B2C (Business to Consumer) | Flywheel |
| Subscription Services | Flywheel |
| High-Ticket Sales | Sales Funnel |
For B2B, the sales funnel works better. It focuses on lead nurturing and closing deals. The flywheel is ideal for B2C and subscription services. It emphasizes customer experience and retention.
Growth Stage Factors
Your business growth stage also matters. Here’s how:
- Startup: Use the sales funnel to acquire customers quickly.
- Growth: The flywheel helps in maintaining momentum and retaining customers.
- Mature: A hybrid approach can be beneficial. Combine both models for balance.
Startups need quick wins. The sales funnel is efficient for this. In the growth stage, customer retention becomes crucial. The flywheel keeps customers engaged. Mature businesses can blend both models. This provides a balanced approach to both acquisition and retention.
Case Studies
Understanding the differences between the sales funnel and the flywheel models is crucial. To help illustrate these concepts, we will look at real-world examples. These case studies show how businesses have successfully implemented both strategies.
Successful Sales Funnel Implementation
Company A, a leading software provider, adopted the sales funnel model. They segmented their customers into three stages: Awareness, Consideration, and Decision.
| Stage | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Content Marketing | Increased website traffic by 40% |
| Consideration | Email Campaigns | Boosted engagement by 25% |
| Decision | Personalized Demos | Improved conversion rates by 30% |
Content Marketing at the awareness stage helped attract potential customers. They used blogs, social media posts, and videos. This strategy led to a 40% increase in website traffic.
During the consideration stage, Email Campaigns played a crucial role. They sent targeted emails with valuable content. This resulted in a 25% boost in engagement.
In the decision stage, they focused on Personalized Demos. They tailored demos to meet specific customer needs. This improved their conversion rates by 30%.
Successful Flywheel Implementation
Company B, an e-commerce retailer, switched to the flywheel model. They focused on delighting customers to drive growth.
- Attraction: Leveraged social proof and user-generated content.
- Engagement: Provided exceptional customer service and fast shipping.
- Delight: Implemented loyalty programs and personalized follow-ups.
In the attraction phase, they leveraged social proof. They highlighted user-generated content. This approach created trust and drew more visitors.
For engagement, they prioritized exceptional customer service. They offered fast shipping and easy returns. This improved customer satisfaction and retention.
In the delight stage, they implemented loyalty programs. They also used personalized follow-ups. These efforts increased repeat purchases and customer referrals.
Both companies saw significant growth by applying these strategies. The sales funnel helped Company A in a structured manner. The flywheel drove continuous growth for Company B through customer delight.
Credit: www.growth-rocket.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Sales Funnel?
A sales funnel represents the customer journey from awareness to purchase. It consists of multiple stages, guiding prospects towards conversion.
What Is The Flywheel Model?
The flywheel model focuses on customer retention and satisfaction. It uses customer feedback to drive growth and improve business processes.
How Do Sales Funnels And Flywheels Differ?
Sales funnels prioritize converting leads into customers. The flywheel, however, emphasizes customer retention and continuous engagement, fostering long-term relationships.
Which Is Better: Sales Funnel Or Flywheel?
The best choice depends on your business goals. Sales funnels drive quick conversions, while flywheels build lasting customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Both the sales funnel and the flywheel have their strengths. The sales funnel focuses on converting leads quickly. The flywheel, on the other hand, emphasizes customer retention. Each business must evaluate its goals and resources. Choose the model that aligns with your objectives.
Happy customers create lasting growth. Understand your audience. Implement the right strategy. Success follows a well-chosen path.